Cybersecurity Tips Part I : Why is Endpoint Protection Software so Important?
This is the first post in a 4-part series of cybersecurity tips. Links to other posts are below.
Malware and Its Impact
A Quick Anti-Malware Story
A client of ours brought a home computer into their office without our knowledge and connected it to their office network. The computer had been used by one of their children and had 67 different malware infected files, services, or registry items. This included ransomware. The computer was so infected that it was flooding the firewall and overloading it, which repeatedly and randomly shut down internet access for the whole office. The firewall logs gave us insight though, so we could track down the problem, but it was frustrating, time consuming, and expensive for our client.
Moral of the story: Use Anti-Malware software, and keep your IT contact informed.
What is Malware?
Malware refers to a variety of forms of hostile or intrusive software. These include computer viruses, worms, trojan horses, ransomware, spyware, adware, scareware, and other malicious programs.
Why do I need Anti-Malware software?
It’s important to protect EVERY computer from malware because it can:
- Steal usernames & passwords, and then use them on other websites
- Send personal information to hackers without you knowing–it’s to their benefit to make sure you never notice anything has happened
- Steal credit card information
- Infect other computers on your network and on the internet
- Encrypt all of the information on your computer – Read “How the cryptolocker virus forces you to pay to get your data back“
What happens if I don’t use Endpoint Protection software?
Hackers use malware to hijack your network or computer, using your computer to do a long list of things that can be found in our post, The Value of a Hacked PC. ClickOrlando published an interview with Malwarebytes CEO Marcin Kleczynski where he states, “The latest way hackers are gaining access to computers is by hiding malware on mainstream websites such as Yahoo and YouTube.”
How big is the problem?
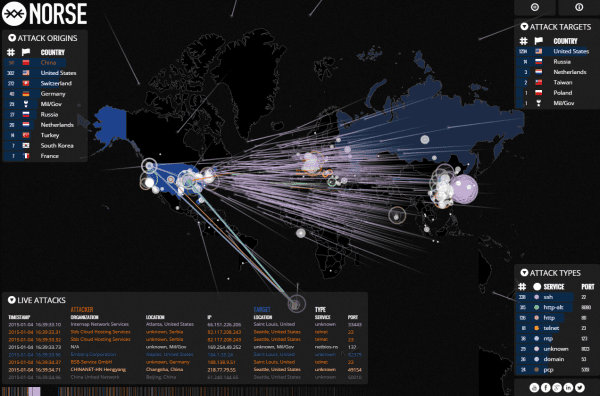
Brian Krebs is a security blogger that just won a National Journalism Award and just posted a Who’s Attacking Who article showing a graphical view of where attacks originate from and what locations are targets. Most attacks are coming from China, Russia, and Europe.
Click the image to view the ACTIVE cybersecurity map.
If you are scanning for malware and malware is not turning up on your machine then someone, some software, and/or some security device is doing a good job of protecting you and it’s most likely a combination of all three.
What To Do
It’s easier than you think.
- Install endpoint detection software, keep it updated, and have it managed by a professional if you don’t have the skills. Webroot is one of the best places to get one that will protect you well if updated and managed properly.
- Get help from an experienced cybersecurity analyst if you’re in unfamiliar territory
- Create a comprehensive security strategy and stick to it
- Don’t deviate from the plan since “nothing is happening” or “some websites are being blocked”
- Keep in mind that cybersecurity is not static. Adjustments need to be made.
- Create and review automated cybersecurity reports
- Contact Us if you need help. Our managed anti-malware solution is part of the remote monitoring and management (RMM) component of our Managed IT platform and is very affordable, easy to implement on a small or large scale, won’t interrupt people’s work, and speeds up computers.
Other Components of a Great Cybersecurity Plan
- Anti-Malware Software
- Managed Firewall
- Ant-Virus Software
- Security Patches & Updates
We will discuss the other cybersecurity tips and the other 3 aspects of a great cybersecurity plan over the next few weeks so stay tuned.